
September 29, 2022 | Article
The Conference Board predicts a 96 percent likelihood of a recession in the US within the next 12 months, based on our probability model. This supports our expectation of a recession before the end of 2022 caused by the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes. The last quarter of 2022 and the first quarter of 2023 are likely to see negative real GDP growth rates.
While recession probability hovered near zero after the initial phase of the global pandemic from September 2020 to March 2022, it rose to over 30 percent in April and reached 50 percent in May (Chart below). This means that the US economy is likely to enter a recession within a year from that point onward. The probability has kept rising since then.
Recession Probabilities at Highest Level Since mid-2020
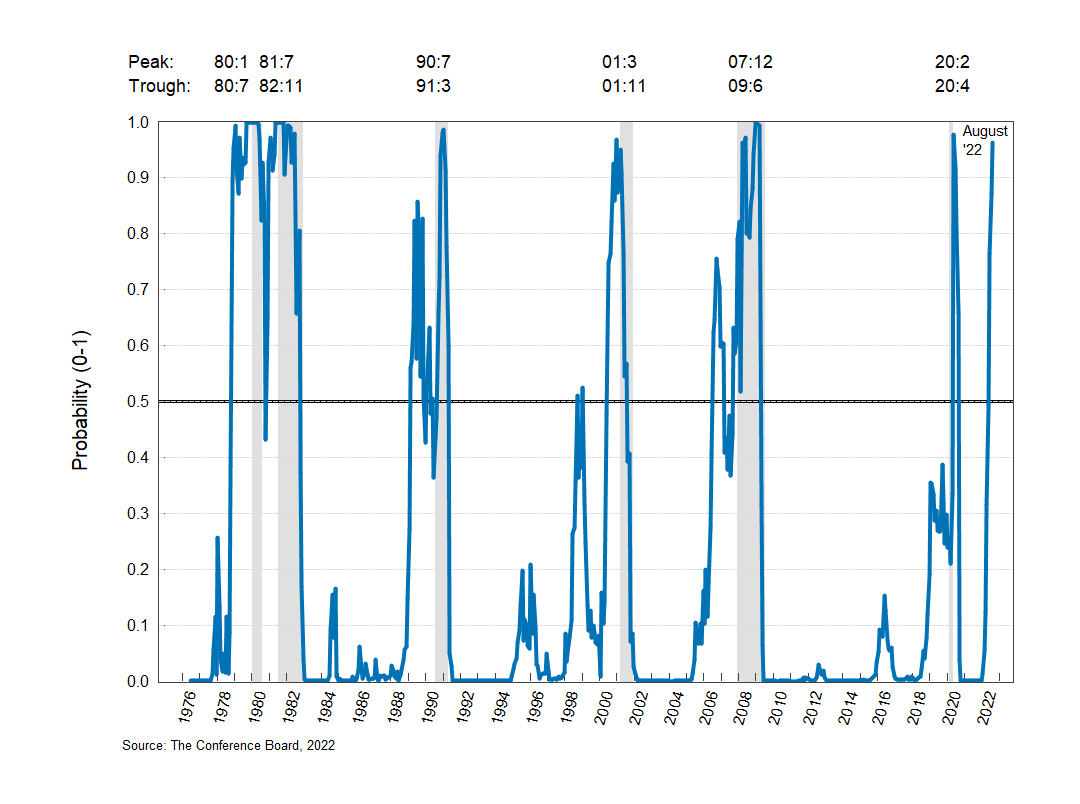
Note: The probability of the US economy being in recession within the next 12 months is estimated by a probit model using the following explanatory variables: the spread between the 10-year Treasury bond yields and the 2-year Treasury bond yields, the six-month growth rate of The Conference Board Leading Economic Index® (LEI) for the US, diffusion index of 10 leading indicators (over six months), National Financial Conditions Index (+=Tighter Than Avg) from the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, and the log changes in the Reserve Bank Credit: US Treasury Securities held Outright (EOP, Mil.$).
What’s Driving the Elevated Probability of a Recession?
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy and financial conditions are playing important roles in the elevated US recession probability in 2022. The probability is estimated using several leading indicators including: 1) the yield spread; 2) financial conditions; and 3) the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet. The variables used in this model are particularly informative about the future state of the economy because they are timely and reflect financial markets’ assessments of future economic conditions.
First, narrowing of the spread between the 10-year Treasury bond yield and the 2-year Treasury bond yield is an indication of tightening monetary policy which becomes contractionary for the economy. It is also an indication that markets expect future economic conditions to worsen.
Second, financial conditions indexes tend to increase ahead of recessions indicating financial instability. Thus, worsening financial conditions raise the probability of a recession. For the national financial conditions index used in our model, positive (negative) values are associated with tighter (looser) conditions relative to the average and raise the probability of a recession. Recently, this variable has shown increasingly tighter conditions and rising financial instability.
Finally, the reduction of US Treasury Securities held outright on the Federal Reserve balance sheet suggests that quantitative easing policies pursued by the Federal Reserve to provide economic stimulus are being reversed (often referred to as “quantitative tightening”).
The variables in the model are supplemented by The Conference Board Leading Economic Index®(LEI) for the US and its diffusion index (which measures the proportion of components that are rising) to represent nonfinancial factors in the broader business cycle. When these measures of the broader business cycle conditions deteriorate, the probability of recession increases. In recent months, each of these factors have supported the rising probability of recession.
When Might the Recession Begin (and End)?
The estimated probabilities also confirm recession signals from other leading indicators, such as the US LEI. For example, in September 2022, the US LEI appeared to show a peak in February 2022 and has been on a downtrend since. Such peaks in the leading index almost always precede business cycle peaks (by 11 to 12 months on average) that herald recessions. The probability model supports this reading from the US LEI but also suggests the recession could potentially start earlier in Q3 or Q4 of 2022.
Recession probability models are also useful in signaling the end of economic downturns. They tend to fall rapidly shortly before recessions end. In other words, the likelihood of the economy being in recession within the next twelve months falls below 50 quickly, usually within one or two months. We will monitor this measure to help assess when the US economy will start climbing out of the imminent recession.

April 23, 2025 | Brief
